Today, PLANT SCIENCE INNOVATIONS are making staple crops more profitable, more nutritious and better protected against unpredictable weather. Cassava is no exception. Both farmers and consumers throughout the world can reap the benefits of varieties that are healthier, heartier and more abundant.
Cassava provides sustenance for over 800 million people. A perennial woody shrub native to Latin America, cassava is primarily grown as an annual crop in the humid tropics. Studies indicate it is the only staple crop that stands to benefit from climate change. As more land is rendered unusable due to changing temperature and rainfall patterns, cassava will likely gain ground as a staple around the globe.
We spoke with Chiedozie Egesi of NextGen Cassava Breeding Project, who is at the forefront of new innovations to enhance this already resilient and hearty staple crop. Read our interview with him to learn how and why cassava is a major staple crop of the developing world and what its future holds. (This interview has been formatted for brevity and clarity.)

Chiedozie Egesi, leader of the NextGen Cassava Breeding Project, tells us how he and his team are developing better cassava plants to resist challenging growing conditions, be more productive and deliver more nutrition.
Tell me about your role at NextGen Cassava. What type of research do you lead?
Our main objective is to empower African cassava farmers through innovative, sustainable cassava breeding. We have begun the process of modernizing cassava breeding institutions in Africa and use cutting-edge tools for efficient delivery of improved varieties of cassava.
My role includes project coordination, charting the course we take and ensuring that our partners are supported to deliver on the project mandate. We specialize in cassava breeding implementation—cutting-edge research technologies that make for more efficient processes and demand-led breeding.
Why is cassava a staple crop in South America, Africa, and other developing countries?
Cassava is a major calorie source for over 800 million people. It has high productivity in marginal environments, making it an invaluable asset for food security—it survives where other crops fail. It also has naturally high resilience to climatic changes. Finally, it is produced mainly by smallholders [farmers with less than 2 hectares of land] – mostly women – with simple technologies, allowing it to be easily grown across multiple countries and environments.
What challenges have cassava farmers faced in recent years?
Cassava producers face several main challenges these days. First, many pests and diseases have constrained production for cassava growers. Part of this is actually because of cassava’s long growth cycle—its long duration in the field increases its exposure to pests and viruses. Also, cassava is perishable, which leads to limited flexibility in handling. Lastly, poorly linked value chains in Africa cause frequent boom-and-bust cycles of high and low productivity. The markets have not been well developed to make for sustainable agribusiness.
How have plant science innovations helped cassava farmers?
A recent example is the timely delivery of new, “best-bet” varieties to cassava farmers. Genomic selection is an integral technology that has enabled us to get these more resilient, more productive and more nutritious varieties. We have employed innovative “citizen science” approaches to enable participatory selection of improved varieties. In addition, new technologies have helped us rapidly screen large breeding populations. Others include techniques to improve flowering in cassava, an essential step for hybridization through pollination. Application of a combination of hormones has enabled us to make cross combinations that were not very easily done due to the poor flowering of some cassava varieties.
Which plant science innovations does NextGen Cassava utilize in its work with smallholder farmers?
We predicted the performance of new varieties based on the genetic information of their parents using modeling systems. This allowed us to reduce the generational cycle time for cassava from about 10 years to five. Better varieties can now get to farmers faster, and we are still working on further improving this. We are designing research that maps preferences and links to social differences such as gender, age, education, region, poverty and food security levels.
How will climate change continue to impact cassava and smallholder farmers?
Cassava is one of the most climate-smart crops in the tropics and has the capacity to withstand changes in the atmosphere, which it can use to its advantage for more productivity. As climate change continues to be a challenge for smallholder growers in Africa, cassava farmers stand a better chance to make more profitable agribusiness due to the robustness of the crop.
How will supporting plant science innovations help communities that depend on cassava?
Support for plant science innovations is needed to help communities that depend on cassava in Africa. New technologies will transform cassava production and deliver the best varieties for maximum impact on growers and their families.
For more information about cassava and its role as a staple crop in different countries around the world, please check out these resources:
Kenya Approves Disease-Resistant Biotech Cassava
In June 2021, the Kenya National Biosafety Authority approved the environmental release of genetically modified cassava, which is resistant to cassava brown streak disease. The disease-resistant cassava was developed under the Virus Resistant Cassava for Africa Plus project, a collaborative program between Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization, National Crops Resources Research Institute of Uganda and Donald Danforth Plant Science Center. Learn more about this breakthrough from the Cornell Alliance for Science and ISAAA.
Repairing the Root of the Problem
Despite the ability to turn cassava into an endless number of palatable dishes, the tuber has two major issues affecting the people who rely on it the most. First, cassava faces the threat of brown streak disease, limiting available food and second, the crop has a natural toxin that can cause severe physical and mental damage in the populations who need it most. For the millions it feeds, this important crop must be usable. That’s where plant biotechnology and gene editing come in. This video from the American Seed Trade Association and University of California at Berkeley shows the research being done to improve this staple crop for the millions who depend on it.
Save and Grow Cassava: A Guide to Sustainable Production Intensification
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations has published a booklet about the production of cassava. It notes that cassava was first cultivated 9,000 years ago on the southern edge of the Brazilian Amazon, where it is still grown. Today, around 300 million tons of cassava are produced globally, with Nigeria as the world’s largest producer. Around 90 percent of harvested roots are destined for human consumption, while about 10 percent are semi-processed on-farm as animal feed. Read the entire 100-page PDF on the FAO website.
African Scientists Improve Cassava to Help Feed the World
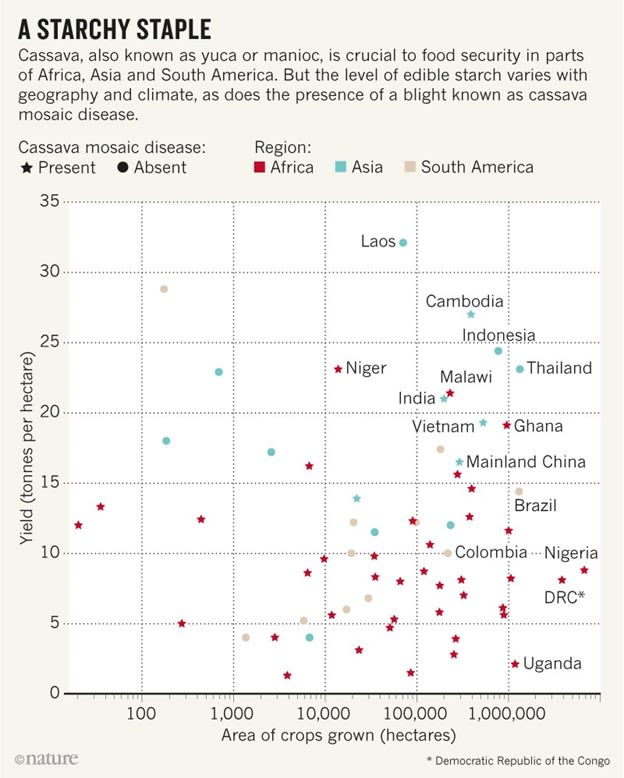
A 2019 article in the journal Nature explains how researchers at the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture in Nigeria are using both traditional breeding and genetic modification to improve the starchy staple crop. In Africa, where consumption is highest, cassava plants bear smaller yields than their cousins in Asia and South America. But African varieties tend to be more tolerant of blights, such as the deadly cassava mosaic disease now spreading across Asia.
Breeding Better Crops, From Maize to Cassava
In this video from the Gates Foundation, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agriculture Research Service (ARS) and Cornell University, plant geneticist Ed Buckler explains that cassava has not been bred as effectively as other crops – such as maize – and there is tremendous potential including disease and insect resistance, by taking new, modern breeding tools and applying them to cassava.
Developing GM Super Cassava For Improved Health and Food Security: Future Challenges in Africa
The potential for GM cassava also includes biofortification. According to a study in the open access journal Agriculture & Food Security, more than 800 million people suffer from micronutrient malnutrition in developing countries with Africa accounting for almost 50 percent of the children who are clinically or sub-clinically deficient in vitamin A, particularly under five years of age. The study found that an overwhelming majority of scientists agree that GM biofortified cassava will benefit the health of millions in Africa and that GM cassava conferred with disease and pest resistance will increase cassava production as it is currently plagued by cassava mosaic diseases (CMD).
